
Carry Trade Explained: A Simple Strategy Guide
Forex trading is like a vast ocean teeming with different strategies and methods. In the dynamic expanse of the financial world, the “carry trade in trading.”, can be considered as one of the most popular trading strategies. In this exploration, we’ll embark on a captivating journey into the realm of the carry trade strategy. This guide aims to provide information on some of the most important elements of the strategy, serving as a wellspring of enlightenment for all those engaged in the art of trading.
What is Carry Trade in trading?
Let’s unravel the essence of the carry trade in trading strategy. Picture this: you’re in a scenario where you borrow some cash from a friend who’s offering it at a pocket-friendly interest rate. Then, you turn around and lend this borrowed sum to another friend, but here’s the twist – you’re charging a notably higher interest rate. The difference or “carry” is your potential profit. The carry trade is essentially the same thing but in the forex trading.
In forex, a carry trade happens when a trader borrows money in a currency with low interest and invests it in a currency with higher interest. The trader then may profit from the difference between the two rates.
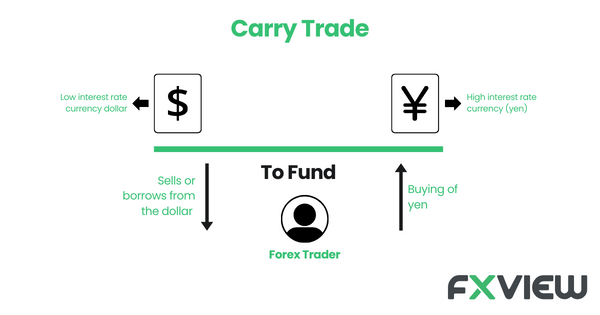
How does Carry Trade in trading strategy work?
Imagine a seesaw. Imagine having two sides: on one, there’s a currency with low interest (the funding currency), and on the other, a currency with high interest (the target currency). The magic of the carry trade strategy revolves around this seesaw action. Here’s the catch: the trader aims to profit from the interest rate difference and any potential price movements in the currencies.
Crucial elements of currency Carry Trade strategy
The foundational pillar of the currency carry trade in trading is the interest rate differential between two currencies. Ideally, one should choose a pair where one currency has a significantly higher interest rate than the other.
How to calculate a Carry Trade in trading?
Let’s get a bit mathematical but keep things simple:
Profit from interest = (Interest rate of the target currency – Interest rate of the funding currency) x Position size
Imagine, the Australian Dollar (AUD) gives you a 3% interest rate, whereas the Japanese Yen (JPY) offers just 0.5%.
If you’re holding $10,000 worth of AUD/JPY, your interest profit would be:
(3% – 0.5%) x $10,000 = $250
Carry Trade Example
Now, let’s take a real-life scenario. Let’s use our AUD/JPY example. A trader decides to buy the AUD while selling the JPY, expecting both a rise in AUD value and potentially profiting from the interest difference. If AUD does appreciate and interest rates remain consistent, the trader may profit from both the currency appreciation and the interest differential.
Risks of Carry Trades
Every rose has its thorns, and the carry trade in trading strategy is no exception. Market volatility can wreak havoc on potential profits. You should always bear in mind that there’s also the peril of interest rate changes by Central Banks, which can turn the tables unexpectedly.
- Interest Rate Fluctuations: Central Banks can change a country’s interest rates to control inflation or boost economic growth. When these rates are changed, it can lead to sudden and dramatic shifts in carry trade dynamics. For instance, if you’re earning a positive carry from borrowing a low-yielding currency and investing in a high-yielding one, a rate hike in the former or a drop in the latter could shrink or even negate this differential.
- Exchange Rate Movements: When you’re involved in carry trade in trading, you’re not just exposed to interest rate differences but also potential shifts in the exchange rate of the paired currencies. If the currency you’ve borrowed appreciates significantly against the one you’ve invested in, the capital loss could easily surpass the interest gain.
- Leverage– A Double-Edged Sword: Leverage in forex allows traders to potentially control a prominent position with a comparatively smaller amount of capital. While this may amplify potential profit in favourable conditions, it could equally magnify losses when the market turns. A minor unfavourable shift, when highly leveraged, can lead to substantial capital erosion.
- Unexpected Twists & Turns in the Market: Forex markets, just like all financial markets, can be affected by unforeseen global events, be they political upheavals, major economic shifts, or even natural disasters. Such events can lead to extreme volatility, making the market move against your carry position swiftly.
- Liquidity Concerns: Sometimes, especially in tumultuous market conditions, you may find it difficult to quickly exit your carry trade position due to reduced market liquidity. This can result in slippage, where the execution price differs from the expected price, exacerbating losses.
- Nation and Economic Risk: The countries behind the currencies involved in your carry trade might face economic concerns, political instability, or other country-specific risks. Such situations can lead to rapid depreciation of the invested currency.
- Crowded Trades and Reversals: Carry trade in trading can become popular when many traders jump onto the bandwagon. However, when too many traders are in on the same strategy, the potential for sharp reversals increases. A mass exodus from a popular carry trade can be particularly damaging if you’re late to exit.
Pros and Cons of Currency Carry Trading
Pros
- Hedging Opportunity: May act as a risk management tool to hedge against other trading positions.
- Interest Income: One of the primary benefits is the daily interest income that traders can earn on their positions, especially if they hold them for an extended period.
- Low Volatility: Typically, high-yielding currencies are from economies that offer stability, making carry trades somewhat less volatile than other forex strategies.
- Diversification: For portfolio managers and individual investors, the carry trade offers a way to diversify strategies and sources of return.
- Predictability: Changes to interest rates are typically well-flagged in advance by central banks. This forward guidance can provide carry traders with a heads-up, allowing them to adjust their positions accordingly.
- High Liquidity: Major currency pairs involved in carry trades (e.g., AUD/JPY, NZD/JPY) generally have high liquidity, ensuring that large positions can be opened and closed without significant slippage.
- Leverage: Most forex brokers offer substantial leverage, which means traders can control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. This magnifies both the potential profits and risks.
- Long-term Strategy: Carry trades can be more of a long-term strategy, requiring less day-to-day management than some other forex trading strategies.
- Benefit from Global Economic Trends: Those who are well-informed about global economic trends can make educated decisions about which countries are likely to raise or lower interest rates, giving an edge in carry trade decisions.
Cons
- Interest Rate Fluctuations: Central Bank decisions can affect rates overnight.
- Leverage Risk: High leverage can amplify both potential gains and losses.
- Risk Management: As with any strategy in the forex market, risk management is crucial to safeguard against potential pitfalls.
- Stay Updated: Keeping an eagle’s eye on global economic news and Central Bank decisions.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: This may limit potential losses.
- Diversify: Don’t put all your eggs in one basket; diversify across different currency pairs.
Conclusion
The essence of the carry trade in trading lies in potentially profiting from the interest rate differential between two currencies. While the carry trade-in trading strategy may offer the potential for profits, it’s not without its share of risks. There is always a high chance of losing the capital invested. Staying informed and using smart risk management are crucial elements of currency carry trade.
Disclaimer: The information contained in this article is provided for educational and informational purposes only and it is not intended to be, nor does it constitute financial, investment or trading advice. You should not make any financial, investment or trading decision based on the information provided in this article without performing your own research or seeking advice from an independent advisor.



